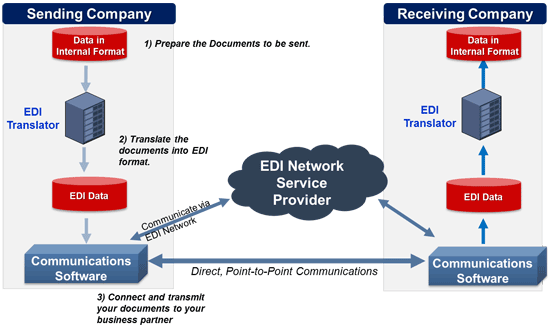
A VAN or value added network can be defined as a network provider hired privately by a company in order to aid and facilitate web EDI (electronic data interchange) and to provide other network services. These services are sometimes also called a turnkey communication line.
Prior to the advent of the World Wide Web, many companies were hiring value added networks in order to move their company data to other companies. Now with the massive use of the internet, companies are finding it more cost-efficient to opt to move their data over the net rather than having to paid monthly fees or per-character charges that were typically found in VAN contracts.
In response to this change in use, modern VAN providers have now shifted their focus by providing services such as encryption, EDI translation, secured e-mail facilities as well as management reports and analysis and several extra services that benefit companies.
Before EDI comes into play, company information is stored on a mainframe or server into a database or using back-end software applications. It is then possible to retrieve data from the outbound EDI transaction and to include outbound data by hand or automatically assuming that the export and import of files are enabled. EDI systems normally bring advantages to companies in terms of cost-savings and work efficiency by eliminating certain tasks and enabling employees to focus on more value-adding activities.